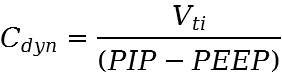Respiratory pressure parameters
Overview
The SPIRO app considers the peak inspiratory pressure (PIP), the positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP), the mean airway pressure (Pmean) and the dynamic compliance (Cdyn).Details
Peak inspiratory pressure (PIP (cmH20))The peak inspiratory pressure is the maximum pressure during ventilation, see [Rimensberger2015] p.302. Depending on the ventilation mode the PIP can represent different respiratory system characteristics.
Note: The PIP value does not only depend on the pressure applied during ventilation. It is also influenced by spontaneous breathing of the patient.
For example in the case of CPAP ventilation (continuous positive airway pressure) without spontaneous breathing, the PIP corresponds to the applied pressure. But with spontaneous breathing the detected PIP value is a mixture of the applied ventilation pressure and the pressure resulting from breathing.
PIP is detected by the software as the maximum pressure during the inspiration phase (thus between an inspiratory and expiratory onset).
Positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP (cmH2O))
PEEP, sometimes also called P-low, is the elevation of the baseline pressure during ventilation, see [Tobin2013] p.49, 89 and [Lucking2012] p.273. The PEEP value is generally a setting of the applied ventilation mode, that maintains the patency of lungs. This is even more important in the ventilation of newborns, than in the ventilation of adults. For newborns there is a concept of physiologic PEEP to avoid airway closure and ventilation-perfusion inequalities.
In ventilated patients the baseline or expiratory pressure is set relative to the atmospheric pressure. Usually the baseline pressure exceeds the atmospheric pressure, resulting in a positive PEEP value.
In this software PEEP is defined as the lowest pressure during the expiration phase (thus between an expiratory and inspiratory onset).
Pressure at onset of inspiration (Poi (cmH2O))
Definition: The pressure at the onset of inspiration (the onset of inspiration is defined by the placement of an inspiratory marker in the START app). In case of mechanical ventilation, this resembles the PEEP.
Pressure at onset of expiration (Poe (cmH2O))
Definition: The pressure at the onset of expiration (the onset of expiration is defined by the placement of an expiratory marker in the START app). In case of mechanical ventilation with a volume-controlled setting, this resembles the PIP.
Lowest inspiratory pressure (LIP (cmH2O))
Definition: The lowest pressure during the inspiration phase (thus between an inspiratory and expiratory onset).
Mean airway pressure (Pmean (cmH2O))
Definition: The mean airway pressure is in general the average airway pressure over a given time interval, see [Rimensberger2015] p.303, 306. As usually, the given time interval is set to one respiratory cycle.
Pmean is calculated as the average airway pressure (Pmask) between two inspiratory onsets.
Dynamic compliance (Cdyn (mL/cmH2O/kg))
Compliance describes the expansion due to a pressure change. The dynamic compliance is a resistive properties of the respiratory system, see [Rimensberger2015] p.312. It relies on the volume- and the pressure change between the end-inspiration and the end-expiration.
The dynamic compliance is calculated as